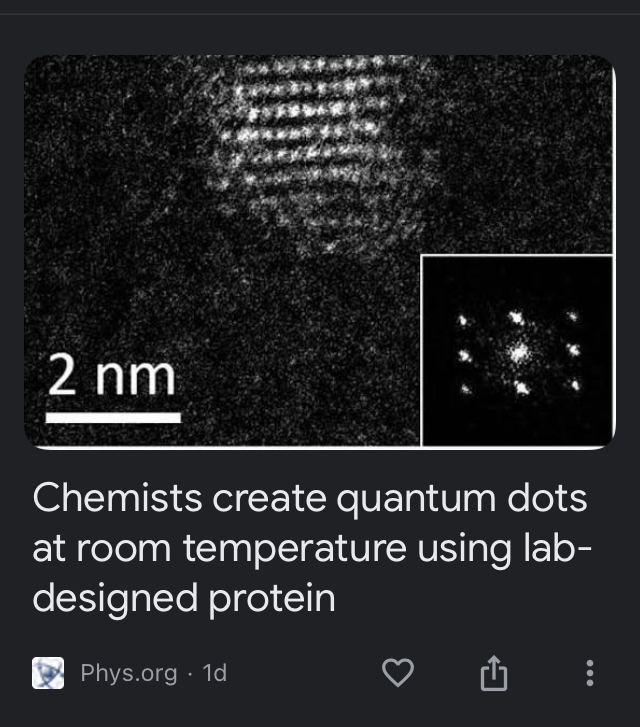
A research group led by Prof. Wu Kaifeng from the Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics (DICP), Chinese Academy of Sciences recently reported the successful initialization, coherent quantum-state control, and readout of spins at room temperature using solution-grown quantum dots, which represents an important advance in quantum information science.
The study was published in Nature Nanotechnology on Dec 19th.
Quantum information science is concerned with the manipulation of the quantum version of information bits (called qubits). When people talk about materials for quantum information processing, they usually think of those manufactured using the most cutting-edge technologies and operating at very cold temperatures (below a few Kelvin), not the "warm and messy" materials synthesized in solution by chemists.
Recent years have witnessed the discovery of isolated defects in solid-state materials (such as NV centers) that have made possible room-temperature spin-qubit manipulation, but scaled-up production of these "point defects" will eventually become a challenge.
Colloidal quantum dots (QDs), which are tiny semiconductor nanoparticles made in solution, could be a game changer. They can be synthesized in large quantities in solution at low cost, yet with high finesse in size and shape control.
Further, they are usually strongly quantum-confined, thus their carriers well isolated from the phonon bath, which could enable long-lived spin coherence at room temperature. But room-temperature coherent manipulation of spins in colloidal QDs has never been reported, in that a QD system whose spins can be simultaneously initialized, rotated, and readout at room-temperature remains to be invented.
Here the authors show that solution-grown CsPbBr3 perovskite QDs can actually accomplish this intimidating goal. Polarized hole spins are obtained by sub-picosecond electron scavenging, to surface-anchored molecular acceptors, following a circularly-polarized femtosecond pulse excitation.
A transverse magnetic field induces coherent Larmor precession of the hole spins. A second off-resonance femtosecond pulse coherently rotates the spins through the optical Stark effect, which is enabled by the exceptionally strong light-matter interaction of the perovskite QDs. These results represent full quantum-state control of single-hole spins at room temperature, holding great promise for a scalable and sustainable future of spin-based quantum information processing
"Our success here is enabled by a very rare combination of knowledge in materials, chemistry and physics," said Prof. Wu. "We fabricated strongly- and uniformly-confined CsPbBr3 QDs as the unique system for the study, and identified appropriate surface-ligand molecules to rapidly extract the electrons via charge-transfer chemistry for hole-spin initialization at room temperature. Meanwhile, we were able to utilize strong light-matter interaction of these QDs to perform coherent spin manipulation."