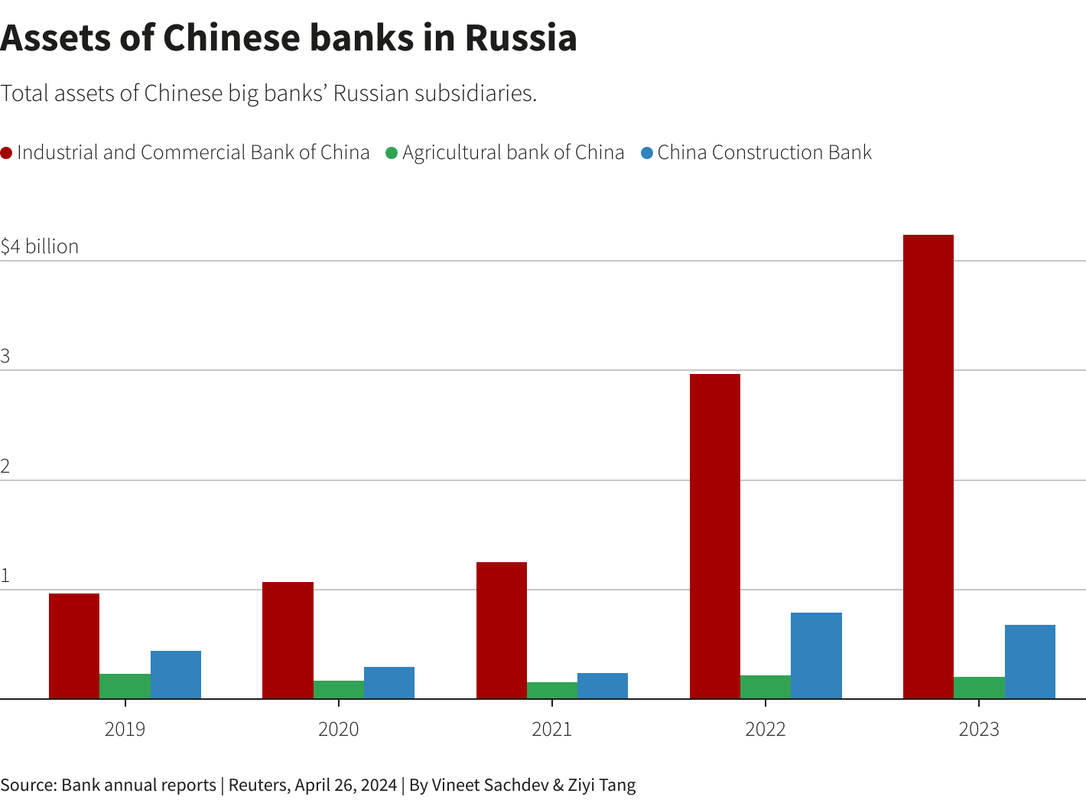
#82 Re: SWIFT and CIPS的情况
发表于 : 2024年 4月 30日 13:24
本币互换额度增大的国/地
2009 年 1 月 20 日, 香港 金融管理局 签署了规模为 2000
1 2011 年 11 月 22 日, 香港 金融管理局 续签双边本币互换协议,互换规模由原来的 2000
2 2014 年 11 月 22 日, 香港 金融管理局 续签了规模为 4000
2 2017 年 11 月 22 日, 香港 金管局 续签双边本币互换协议,协议规模为 4000
2.5 2020 年 11 月 23 日, 香港 金融管理局 签署双边本币互换修订协议将互换规模扩大为 5000
4 2022 年 7 月 1 日, 香港 金融管理局 签署常备互换协议,并将双边本币互换规模扩大至 8000
2013 年 9 月 9 日, 匈牙利 中央银行 签署了规模为 100
1 2016 年 9 月 12 日, 匈牙利 央行 续签双边本币互换协议,协议规模为 100
2 2019 年 12 月 10 日, 匈牙利 中央银行 续签规模为 200
4 2020 年 9 月 17 日, 匈牙利 中央银行 签署规模为 400
4 2022 年 12 月 10 日, 匈牙利 中央银行 续签规模为 400
2012 年 2 月 21 日, 土耳其共和国 中央银行 签署了规模为 100
1.2 2015 年 9 月 26 日, 土耳其共和国 中央银行 续签了规模为 120
1.2 2019 年 5 月 30 日, 土耳其共和国 中央银行 续签规模为 120
3.5 2021 年 6 月 4 日, 土耳其共和国 中央银行 签署双边本币互换修订协议将互换规模扩大为 350
3.5 2022 年 6 月 6 日, 土耳其共和国 中央银行 续签规模为 350
2011 年 5 月 6 日, 蒙古 银行 签署了规模为 50
1 2012 年 3 月 20 日, 蒙古 银行 签署了中蒙双边本币互换补充协议,互换规模由原来的 50
3 2014 年 8 月 21 日, 蒙古 银行 续签了规模为 150
3 2017 年 7 月 6 日, 蒙古 银行 续签双边本币互换协议,协议规模为 150
3 2020 年 7 月 31 日, 蒙古 银行 续签规模为 150
3 2023 年 7 月 31 日, 蒙古 银行 续签规模为 150
2011 年 12 月 23 日, 巴基斯坦 国家银行 签署了中巴双边本币互换协议,互换规模为 100
1 2014 年 12 月 23 日, 巴基斯坦 国家银行 续签了规模为 100
2 2018 年 5 月 23 日, 巴基斯坦 国家银行 续签规模为 200
3 2020 年 7 月 31 日, 巴基斯坦 国家银行 签署双边本币互换修订协议将互换规模扩大为 300
3 2021 年 7 月 13 日, 巴基斯坦 国家银行 续签规模为 300
2009 年 3 月 23 日, 印度尼西亚 银行 签署了规模为 1000
1 2013 年 10 月 1 日, 印度尼西亚 银行 续签了规模为 1000
2 2018 年 11 月 16 日, 印度尼西亚 银行 续签规模为 2000
2.5 2022 年 1 月 21 日, 印度尼西亚 银行 续签规模为 2500
2015 年 5 月 25 日, 智利 中央银行 签署了在智利建立人民币清算安排的合作备忘录,并签署了规模为 220
1 2018 年 5 月 25 日, 智利 中央银行 续签规模为 220
2.272727273 2020 年 7 月 31 日, 智利 中央银行 签署双边本币互换修订协议将互换规模扩大为 500
2.272727273 2021 年 8 月 20 日, 智利 中央银行 续签规模为 500
2009 年 2 月 8 日, 马来西亚 国家银行 签署了规模为 800
1 2012 年 2 月 8 日, 马来西亚 国家银行 续签了中马双边本币互换协议,互换规模由原来的 800
2.25 2015 年 4 月 17 日, 马来西亚 国家银行 续签了规模为 1800
2.25 2018 年 8 月 20 日, 马来西亚 国家银行 续签规模为 1800
2.25 2021 年 7 月 12 日, 马来西亚 银行 续签规模为 1800
2009 年 4 月 20 日, 韩国 银行 签署了规模为 1800
1 2011 年 10 月 26 日, 韩国 银行 续签双边本币互换协议,互换规模由原来的 1800
2 2014 年 10 月 11 日, 韩国 银行 续签了规模为 3600
2 2017 年 10 月 11 日, 韩国 银行 续签双边本币互换协议,协议规模为 3600
2.222222222 2020 年 10 月 11 日, 韩国 银行 签署双边本币互换展期与修订协议将互换规模扩大为 4000
2010 年 7 月 23 日, 新加坡 金融管理局 签署了规模为 1500
2 2013 年 3 月 7 日, 新加坡 金融管理局 续签了规模为 3000
2 2016 年 3 月 7 日, 新加坡 金管局 续签双边本币互换协议,协议规模为 3000
2 2019 年 5 月 10 日, 新加坡 金融管理局 续签规模为 3000
2 2022 年 7 月 13 日, 新加坡 金融管理局 续签规模为 3000
2009 年 4 月 2 日, 阿根廷 中央银行 签署了规模为 700
1 2014 年 7 月 18 日, 阿根廷 中央银行 续签了规模为 700
1 2017 年 7 月 18 日, 阿根廷 央行 续签双边本币互换协议,规模为 700
1 2020 年 8 月 6 日, 阿根廷 中央银行 续签规模为 700
1.857142857 2023 年 6 月 9 日, 阿根廷 中央银行 续签规模为 1300
2013 年 6 月 22 日, 英格兰 银行 签署了规模为 2000
1.75 2015 年 10 月 20 日, 英格兰 银行 续签了规模为 3500
1.75 2018 年 10 月 13 日, 英格兰 银行 续签规模为 3500
1.75 2021 年 11 月 12 日, 英格兰 银行 续签规模为 3500
2009 年 1 月 20 日, 香港 金融管理局 签署了规模为 2000
1 2011 年 11 月 22 日, 香港 金融管理局 续签双边本币互换协议,互换规模由原来的 2000
2 2014 年 11 月 22 日, 香港 金融管理局 续签了规模为 4000
2 2017 年 11 月 22 日, 香港 金管局 续签双边本币互换协议,协议规模为 4000
2.5 2020 年 11 月 23 日, 香港 金融管理局 签署双边本币互换修订协议将互换规模扩大为 5000
4 2022 年 7 月 1 日, 香港 金融管理局 签署常备互换协议,并将双边本币互换规模扩大至 8000
2013 年 9 月 9 日, 匈牙利 中央银行 签署了规模为 100
1 2016 年 9 月 12 日, 匈牙利 央行 续签双边本币互换协议,协议规模为 100
2 2019 年 12 月 10 日, 匈牙利 中央银行 续签规模为 200
4 2020 年 9 月 17 日, 匈牙利 中央银行 签署规模为 400
4 2022 年 12 月 10 日, 匈牙利 中央银行 续签规模为 400
2012 年 2 月 21 日, 土耳其共和国 中央银行 签署了规模为 100
1.2 2015 年 9 月 26 日, 土耳其共和国 中央银行 续签了规模为 120
1.2 2019 年 5 月 30 日, 土耳其共和国 中央银行 续签规模为 120
3.5 2021 年 6 月 4 日, 土耳其共和国 中央银行 签署双边本币互换修订协议将互换规模扩大为 350
3.5 2022 年 6 月 6 日, 土耳其共和国 中央银行 续签规模为 350
2011 年 5 月 6 日, 蒙古 银行 签署了规模为 50
1 2012 年 3 月 20 日, 蒙古 银行 签署了中蒙双边本币互换补充协议,互换规模由原来的 50
3 2014 年 8 月 21 日, 蒙古 银行 续签了规模为 150
3 2017 年 7 月 6 日, 蒙古 银行 续签双边本币互换协议,协议规模为 150
3 2020 年 7 月 31 日, 蒙古 银行 续签规模为 150
3 2023 年 7 月 31 日, 蒙古 银行 续签规模为 150
2011 年 12 月 23 日, 巴基斯坦 国家银行 签署了中巴双边本币互换协议,互换规模为 100
1 2014 年 12 月 23 日, 巴基斯坦 国家银行 续签了规模为 100
2 2018 年 5 月 23 日, 巴基斯坦 国家银行 续签规模为 200
3 2020 年 7 月 31 日, 巴基斯坦 国家银行 签署双边本币互换修订协议将互换规模扩大为 300
3 2021 年 7 月 13 日, 巴基斯坦 国家银行 续签规模为 300
2009 年 3 月 23 日, 印度尼西亚 银行 签署了规模为 1000
1 2013 年 10 月 1 日, 印度尼西亚 银行 续签了规模为 1000
2 2018 年 11 月 16 日, 印度尼西亚 银行 续签规模为 2000
2.5 2022 年 1 月 21 日, 印度尼西亚 银行 续签规模为 2500
2015 年 5 月 25 日, 智利 中央银行 签署了在智利建立人民币清算安排的合作备忘录,并签署了规模为 220
1 2018 年 5 月 25 日, 智利 中央银行 续签规模为 220
2.272727273 2020 年 7 月 31 日, 智利 中央银行 签署双边本币互换修订协议将互换规模扩大为 500
2.272727273 2021 年 8 月 20 日, 智利 中央银行 续签规模为 500
2009 年 2 月 8 日, 马来西亚 国家银行 签署了规模为 800
1 2012 年 2 月 8 日, 马来西亚 国家银行 续签了中马双边本币互换协议,互换规模由原来的 800
2.25 2015 年 4 月 17 日, 马来西亚 国家银行 续签了规模为 1800
2.25 2018 年 8 月 20 日, 马来西亚 国家银行 续签规模为 1800
2.25 2021 年 7 月 12 日, 马来西亚 银行 续签规模为 1800
2009 年 4 月 20 日, 韩国 银行 签署了规模为 1800
1 2011 年 10 月 26 日, 韩国 银行 续签双边本币互换协议,互换规模由原来的 1800
2 2014 年 10 月 11 日, 韩国 银行 续签了规模为 3600
2 2017 年 10 月 11 日, 韩国 银行 续签双边本币互换协议,协议规模为 3600
2.222222222 2020 年 10 月 11 日, 韩国 银行 签署双边本币互换展期与修订协议将互换规模扩大为 4000
2010 年 7 月 23 日, 新加坡 金融管理局 签署了规模为 1500
2 2013 年 3 月 7 日, 新加坡 金融管理局 续签了规模为 3000
2 2016 年 3 月 7 日, 新加坡 金管局 续签双边本币互换协议,协议规模为 3000
2 2019 年 5 月 10 日, 新加坡 金融管理局 续签规模为 3000
2 2022 年 7 月 13 日, 新加坡 金融管理局 续签规模为 3000
2009 年 4 月 2 日, 阿根廷 中央银行 签署了规模为 700
1 2014 年 7 月 18 日, 阿根廷 中央银行 续签了规模为 700
1 2017 年 7 月 18 日, 阿根廷 央行 续签双边本币互换协议,规模为 700
1 2020 年 8 月 6 日, 阿根廷 中央银行 续签规模为 700
1.857142857 2023 年 6 月 9 日, 阿根廷 中央银行 续签规模为 1300
2013 年 6 月 22 日, 英格兰 银行 签署了规模为 2000
1.75 2015 年 10 月 20 日, 英格兰 银行 续签了规模为 3500
1.75 2018 年 10 月 13 日, 英格兰 银行 续签规模为 3500
1.75 2021 年 11 月 12 日, 英格兰 银行 续签规模为 3500